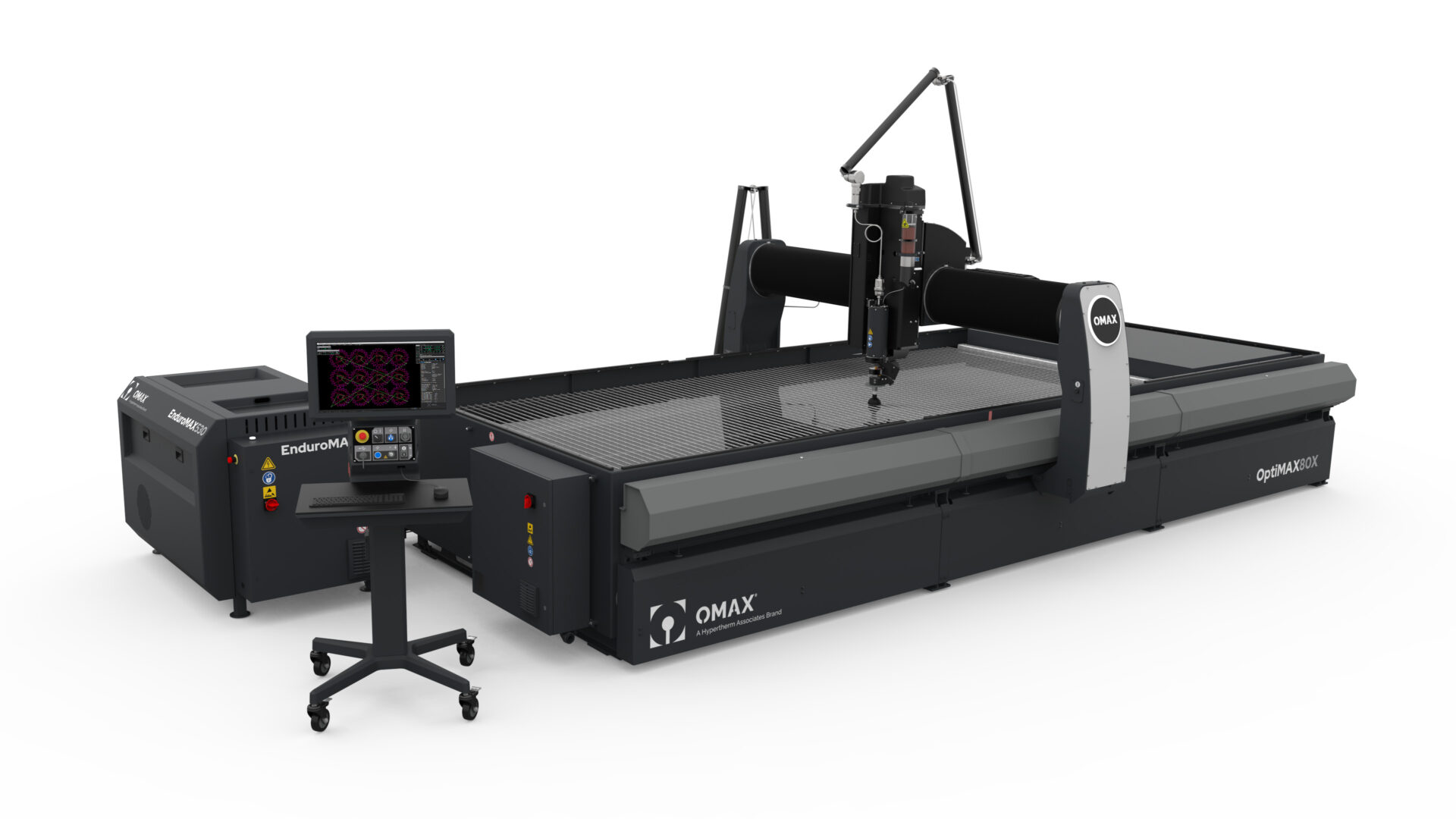

About Waterjets
What Is a Waterjet?
A waterjet utilizes a high-pressure stream of water to erode a narrow line in the stock material. Because the abrasive is added at the nozzle, it is simple to switch between water only and abrasive waterjet cutting. This flexibility greatly enhances the versatility of a waterjet machine, as it can easily switch from cutting ½" (1.27cm) foam gaskets to 4" (10.16cm) titanium brackets.
The waterjet cutting machine system consists of three basic components:
What Industries Use Waterjet Cutters?
Waterjets play a crucial role in producing a diverse range of products across various industries, from jewelry making to aerospace. The adaptability of abrasive cutting and the user-friendly features of contemporary waterjet software make these tools indispensable in numerous fields. Here are some areas where abrasive waterjets shine:
Our user-friendly abrasive waterjets expand your shop's capabilities, enabling you to cut or machine an extensive array of materials with the speed and accuracy demanded by different industries.
Perfect for both instruction and research, our waterjets act as essential learning tools in high schools, trade schools, colleges, and university engineering and physics labs.
Abrasive waterjet cutting provides notable benefits when working with carbon fiber. There's no requirement for tool changes or special measures to prevent heat buildup, melting, or hazardous fumes, thus avoiding the need for expensive air handling systems. Any fiber-reinforced material, including Kevlar-reinforced personnel armor, can be swiftly and cleanly cut, surpassing the limitations of conventional machining methods.
From the orange juice you drink at breakfast to the fish filet you have for dinner, abrasive waterjets are instrumental in creating the machines that process many of your favorite foods.
The adaptability of abrasive waterjets enables the cutting of a wide range of materials and thicknesses without any distortion. Whether working with aluminum, steel, or titanium, you can fulfill any order without switching tools. Our advanced waterjet systems are designed to cut materials from ¼ inch to 3 inches thick. With appropriate adjustments for taper, waterjets can even cut thicker materials, ensuring precision and efficiency for any task.
How Do Waterjets Work?
Waterjet cutting systems operate by pressurizing water, often mixed with abrasives, to high levels using either hydraulic intensifier pumps or crankshaft-driven triplex plunger pumps. Hydraulic intensifiers historically provided durability but are less efficient (around 65%), whereas crankshaft pumps offer higher efficiency (85-90%) due to direct mechanical drive, delivering more power to the cutting nozzle. The pressurized water exits through a precision nozzle, controlled by CNC, to create a focused jet capable of cutting various materials with high precision, minimal heat impact, and reduced maintenance intervals, making waterjets ideal for diverse industrial applications.
Operating Principles of Abrasive Waterjet Nozzles
Abrasive waterjet nozzles operate based on principles dating back to the liquid blasting nozzle patented in 1936 (Patent 2,040,715). A modern configuration includes a jewel orifice carefully aligned within the nozzle body to ensure efficient cutting and extended component life. For water-only nozzles used in cutting soft materials, the mixing chamber and tube are omitted, allowing a coherent jet of water to perform the cutting. OMAX nozzles, for instance, are meticulously factory-aligned and individually tested to maintain high cutting efficiency and durability.
What Materials Can Waterjets Cut?
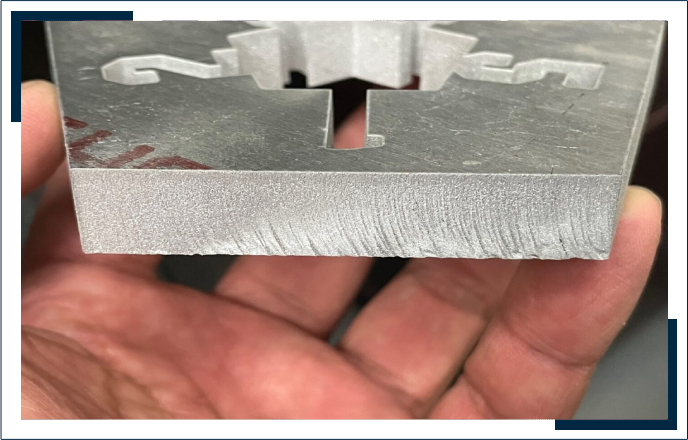
Waterjet machines excel at cutting a wide range of metals, including hardened tool steel, aluminum, titanium, and various exotic metals that pose challenges for other cutting methods. This cold cutting process ensures smooth edges without burn marks, cracking, or excessive burrs, preserving the integrity of the material. Additionally, waterjet cutting eliminates heat-affected zones, making it ideal for applications where material properties must remain unaffected by thermal stress.
How Do Waterjets Compare?
Comparative Analysis of Cutting Methods
| WATERJET | WIRE EDM | LASER | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACCURACY | Average of ±0.003" (±0.08 mm) and up to 0.001” (±25 μ) 1 | ±0.0001" (±2.5 μ) | ±0.001" (±25 μ) 2 2 |
| THICKNESS | Up to 24" (61cm), virtually any material | 12" (30 cm) | Generally less than 0.25"(6.35mm) |
| CUTTING | |||
| SPEED" | 5-10 times faster than EDM when thickness is under 1" | 5-10 times slower than waterjet | Very fast cutting in thin, non-reflective materials |
| EDGE | |||
| QUALITY" | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| MATERIAL | |||
| DISTORTION" | No Distortion 3 | No | Possible |
| HEAT | |||
| AFFECTED | |||
| ZONE (HAZ)" | None | Some | Yes |
| MATERIAL | |||
| LIMITATIONS" | Works in virtually all materials except really hard ceramics | Only works in conductive materials | Only non-reflective metals 4 |
| PROCESS | Cold supersonic abrasive used to cut material | Spark erosion used to remove material from electrically conductive materials | Thermal process |
| SETUP | Fast and easy set-up | Relatively easy set-up | Relatively easy set-up but may have to tune laser for different materials |
